EDL acquisitions are one of many ways you can bypass passcodes and gain physical access to many Android devices with Qualcomm based chipsets. Emergency Download (EDL) mode is a Qualcomm feature that can allow you to recover data from a device and perform tasks like unbricking or flashing the device. On supported devices, we can use EDL to extract a full image.
Read MoreBootloader versus bootrom? Commonly confused, we often need to set the record straight during embedded device assessments.
Read MoreDid you know SIM cards can run applications? SIM cards have built-in functionality that is surprisingly robust. Forensic examination of a SIM card is a clue to uncovering advanced malicious activity on a mobile device.
Read MoreThis guide is a collection of the most common vulnerabilities found in iOS applications.
Read MoreThe open source BioEncrypt SDK contains the fourth authentication factor that most haven’t considered. The fourth factor encompasses the most critical and unique feature of the user… their behavior.
Read MoreSmartphones are susceptible to perhaps the widest range of attacks of any computing device, from sophisticated hackers to muggers. In every mobile pen test we’ve performed, we always gained access to sensitive data and applications—or worse. We’ve even tunneled into clients’ internal networks through no more than an employee’s BYO device. We’ve learned what works, what doesn’t, and what was missing entirely in mobile security.
Read MoreIf developers clone directly into the webroot during push of an application or website, meta-data left behind by Git repo management can be abused to download all of the application’s source code files. These types of issues can be identified by browsing to particular pages. If these pages return any information at all, its likely that your application can and has been downloaded in the past.
Read MoreAWS EC2 has a feature called the Instance Metadata Service. This enables any EC2 instance to access a REST API running on 169.254.169.254, which returns data about the instance itself. An SSRF vulnerability can employ this technique to acquire credentials for AWS services.
Read MoreAs of today, any application on the Apple iOS mobile platform can determine your location and uniquely fingerprint your mobile activity without any indication or user authorization. Even the most innocent-looking applications can gather personal information in this manner.
Read MoreWe perform a wide variety of embedded device assessments. While each device is unique, most tend to follow a pattern that is even more predictable in older devices. Newer medical devices and other embedded systems have become more complex, but in their roots they following basic PC principals. The exception? This PC contains many secrets hidden within and it is much hared to extract them than simply removing a hard drive.
Read MoreTraditional authentication methods were set up for consistency. Whether your account is being accessed from your home computer or from a Russian café, if it was configured for passwords it would ask for the password. As risk-aware creatures, we understand the major risk difference here, so the idea of adaptive authentication was born to help machines make the same determinations.
Read MoreLow-level languages and compiled applications will be around forever, the performance and efficiency compared to high-level “safer” language is still unrivaled. As a result, vulnerabilities stemming from memory corruption are around to stay. Once you understand the basics, you will come to appreciate the sophistication and the complexity involved in preventing memory management bugs and why they will exist forever.
Read MoreBioEncrypt uses sensory data from the device and machine learning to establish trusted user behavior. BioEncrypt uses these TrustFactors to validate the user identity, compute the overall security risk and chose the most appropriate authentication method.
Read MoreDevelopers are waking up to the risks of blindly trusting the underlying device and OS to provide security for their apps. Communities of applications are taking steps to secure their applications in a sandbox’ed environment where malware and legitimate applications are treated equally.
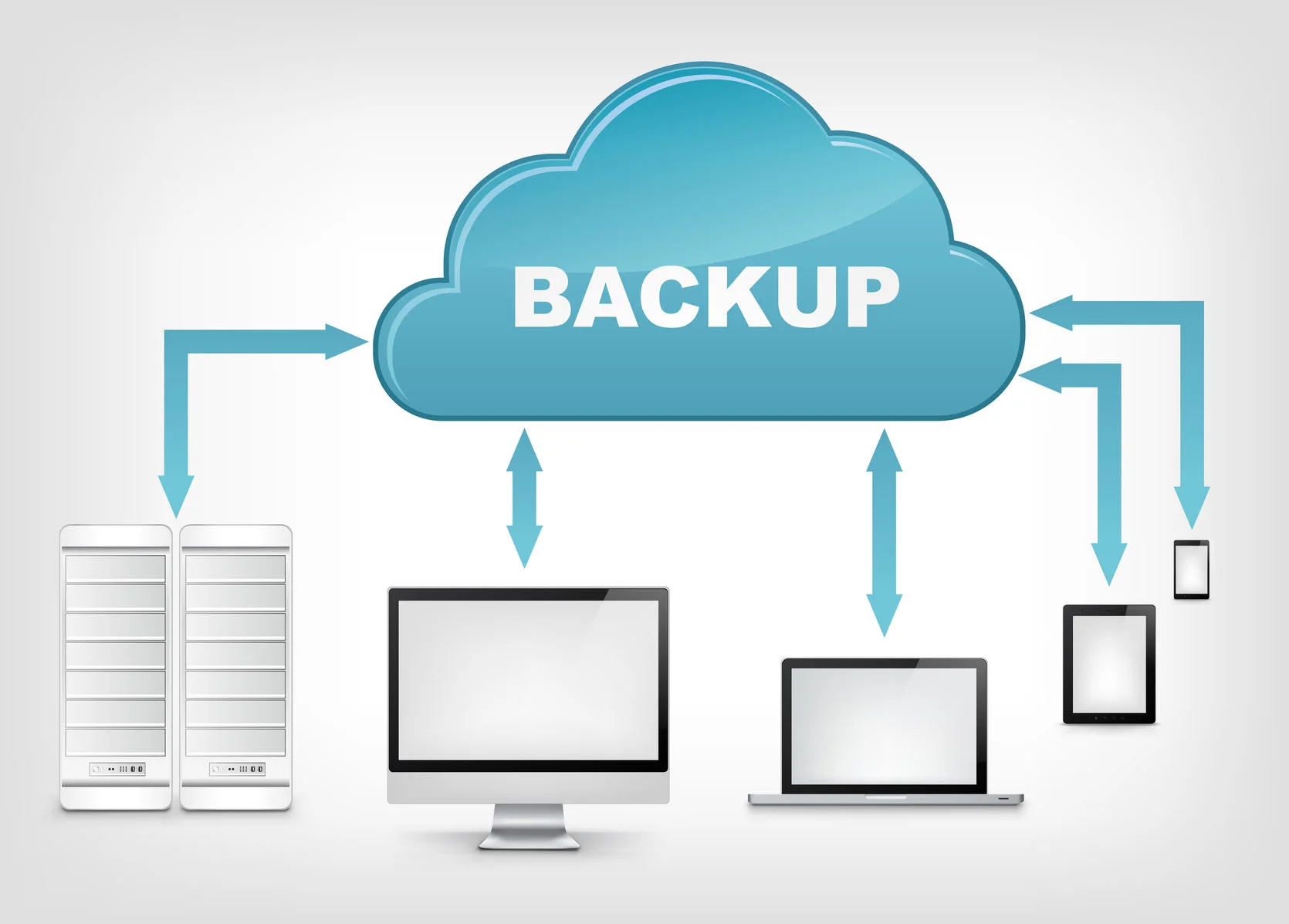
Read MoreAll mobile device’s include data backup capabilities. In most cases two forms of backup exist local and cloud based. Local backups are performed when mobile devices are connected to home PCs over USB and cloud based backups occur continuously on the mobile device using Wi-Fi or Cellular connections. Backup solutions store all kinds of sensitive data completely unknown to the mobile applications that may own it. As a result, sensitive data is essentially replicated to devices out of the control of the application or organization (BYOD). Regardless of whether an application’s data is encrypted or unencrypted at rest, it is all backed up. This includes all data stored within apps, emails, and attachments.
Read MoreMost sensitive mobile apps employ user supplied input to derive encryption keys that grant access to sensitive data and/or functionality, making them the single weakest link in the mobile security chain. Mobile devices magnify the credential problem due to keyboard mechanics that greatly decrease keyspace, and the use of multiple passwords for different apps and the device itself result in excessive password re-use.
Read More